5 Your manager has heard of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory and how it has some relevance to motivational techniques.Required:(a) Explain Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (10 marks)
题目
5 Your manager has heard of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory and how it has some relevance to motivational techniques.
Required:
(a) Explain Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (10 marks)
相似考题
更多“5 Your manager has heard of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory and how it has some relevance to motivational techniques.Required:(a) Explain Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory. (10 marks)”相关问题
-
第1题:
There's still no () evidence that supports the scientist's theory.A、clear
B、obvious
C、valid
D、true
参考答案:C
-
第2题:
1 Flavours Fine Foods is a leading producer for the food industry, supplying many of Europe’s leading restaurants.
Started just five years ago by brothers Lee and Alan Jones, the organisation has grown from a small company employing five people to a multi-divisional organisation employing 120 people.
The organisation’s production facility is divided into three separate departments. Each department has a single manager with supervisors assisting on the production lines. The managers and supervisors, all of whom are aware of their roles, work well together. However, although the organisation has grown, the owners continue to involve themselves in day to day activities and this has led to friction between the owners, managers and supervisors.
As a result a problem arose last week. Alan Jones instructed a supervisor to repair a machine on the shop floor, which he refused to do without confirmation and instruction from his departmental manager. The supervisor’s manager,Dean Watkins, became involved and was annoyed at what he saw as interference in his department’s activities. Dean told Alan Jones that he “should have come to me first” because although the responsibility for the overall organisation was a matter for the brothers, action taken in the factory was his through powers that had been delegated to him and through his authority, as manager. In the argument that followed, Alan Jones was accused of failing to understand the way that the hierarchy in such a large organisation operates and that interference with operational decisions by senior management was not helpful.
As a consequence of this, Alan Jones has asked you to explain to him and his brother the issues behind the dispute to clarify the roles of managers and supervisors and to indicate how and why successful delegation might be achieved.
Required:
(a) Explain to Alan Jones the main differences between the work of a manager and that of a supervisor.
(13 marks)
正确答案:
1 All organisations of whatever size need to understand and address the issues of the relationship between various levels of management, especially the nature, source and limitations of authority, responsibility and delegation. Understanding responsibility,delegation and authority is fundamental to the practice of management. Professional accountants should be able to show an understanding of the problems and challenges associated with these concepts of management. Students are not expected to
remember definitions verbatim, but they are expected to show an understanding of the inherent logic contained in these concepts,and to demonstrate a clear distinction between the two main concepts of authority and responsibility.
(a) There are many explanations of what managers do. The most widely understood approach is that of Henri Fayol, who said that managers perform. five duties, to forecast and plan, to organise, to command, co-ordinate and control. Managers are ultimately responsible for the efficient use of the organisation’s resources and are accountable to the organisation’s owners. At Flavours Fine Foods, the owners (the Jones brothers) must recognise this reality and allow the managers to manage.
It used to be said that a manager did his or her job by getting others to do theirs. In many ways this sums up the role of the supervisor. However, management must ensure that supervisors understand organisational objectives and must make clear the powers and limits of the supervisors’ authority. Supervision is an important and integral part of the task and process of management.
The role of the supervisor is critical because of direct contact with and responsibility directly for the work of others. The supervisor is unique; he or she is the interface between management and the workforce and is the direct link between the two, being in direct physical contact with non-managers on a frequent basis. Supervisors are in the front line of management and see that others fulfil their duties, resolve problems first hand and often quickly, direct the work of others and enforce discipline. In addition, they often must have direct knowledge of health, safety and employment legislation and have authority for negotiation and industrial relations within the department. -
第3题:
(b) How can Maslow’s theory be applied to the motivation of staff? (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) This theory is based on the idea that the goals of the individual and the organisation can be integrated and that personal satisfaction can be achieved through the workplace. It also assumes that individuals will achieve self-actualisation through their role in assisting the organisation to achieve its objectives. It follows therefore that work is the principal source of satisfaction.
The theory’s practical application is that managers should recognise that subordinates’ needs are always evolving and increasing, so continued attention to increasing the employees’ personal development, opportunities for advancement and recognition of achievement are essential to keep them motivated.
-
第4题:
(ii) How existing standards could be modified to meet the needs of SMEs. (6 marks
正确答案:
(ii) The development of IFRSs for SMEs as a modification of existing IFRSs
Most SMEs have a narrower range of users than listed entities. The main groups of users are likely to be the owners,
suppliers and lenders. In deciding upon the modifications to make to IFRS, the needs of the users will need to be taken
into account as well as the costs and other burdens imposed upon SMEs by the IFRS. There will have to be a relaxation
of some of the measurement and recognition criteria in IFRS in order to achieve the reduction in the costs and the
burdens. Some disclosure requirements, such as segmental reports and earnings per share, are intended to meet the
needs of listed entities, or to assist users in making forecasts of the future. Users of financial statements of SMEs often
do not make such kinds of forecasts. Thus these disclosures may not be relevant to SMEs, and a review of all of the
disclosure requirements in IFRS will be required to assess their appropriateness for SMEs.
The difficulty is determining which information is relevant to SMEs without making the information disclosed
meaningless or too narrow/restricted. It may mean that measurement requirements of a complex nature may have to be
omitted.
There are, however, rational grounds for justifying different treatments because of the different nature of the entities and
the existence of established practices at the time of the issue of an IFRS.
-
第5题:
6 The explosive growth of investing and raising capital in the global markets has put new emphasis on the development
of international accounting, auditing and ethical standards. The International Federation of Accountants (IFAC) has
been at the forefront of the development of the worldwide accountancy profession through its activities in ethics,
auditing and education.
Required:
Explain the developments in each of the following areas and indicate how they affect Chartered Certified
Accountants:
(a) IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’; (5 marks)
正确答案:
6 DEVELOPMENTS AND CERTIFIED CHARTERED ACCOUNTANTS
Tutorial note: The answer which follows is indicative of the range of points which might be made. Other relevant material will
be given suitable credit.
(a) IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’
Since its issue in 1996, IFAC’s ‘Code of Ethics for Professional Accountants’ (‘The Code’) has undergone several revisions
(1996, 1998, 2001, 2004 and 2005). IFAC holds the view that due to national differences (of culture, language, legal and
social systems) the task of preparing detailed ethical requirements is primarily that of the member bodies in each country
concerned (and that they also have the responsibility to implement and enforce such requirements).
In recognizing the responsibilities of the accountancy profession, IFAC considers its own role to be in providing guidance and
promoting harmonization. IFAC has established ‘The Code’ to provide a basis on which the ethical requirements for
professional accountants in each country should be founded.
IFAC’s conceptual approach is principles-based. It provides a route to convergence that emphasises the profession’s integrity.
This approach may be summarised as:
■ identifying and evaluating circumstances and relationships that create threats (e.g. to independence); and
■ taking appropriate action to:
– eliminate these threats; or
– reduce them to an acceptable level by the application of safeguards.
If no safeguards are available to reduce a threat to an acceptable level an assurance engagement must be refused or
discontinued.
This approach was first introduced to Section 8 of The Code, on independence, and is applicable to assurance engagements
when the assurance report is dated on or after 31 December 2004.
Further to the cases of Enron, Worldcom and Parmalat, IFAC issued a revised Code in July 2005 that applies to all professional
accountants, whether in public practice, business, industry or government2.
A member body of IFAC may not apply less stringent standards than those stated in the Code. The Code is effective from
30 June 2006.
Practicing accountants and members in business must maintain the high standards of professional ethics that are expected
by their professional bodies (such as ACCA). These developments codify current best practice in the wake of the
aforementioned recent corporate scandals.
The developments in The Code have wider application in that it:
■ applies to all assurance services (not just audit);
■ considers the standpoints of the firm and of the assurance team.
Since ACCA is a member-body of IFAC the elevation of The Code to a standard will affect all Chartered Certified Accountants.
. -
第6题:
We do not yet fully understand the implications of Einstein's______(relate)theory.
正确答案:
relativity[解析] relativity theory:相对论。
-
第7题:
To organize a persuasive message. follow these steps:
(1) gain the reader' s attention. (2) show the reader that he or she has a need. (3) explain your solution to that
need , (4) present the supporting information and (5) end by asking for a specific action.
参考答案:建构一个说服性信息要遵循以下步骤:(1)吸引读者注意力 ;(2) 向读者展示他(她)的需求 ;(3)解释你对该需求的解决办法;(4)提供补充信息 ;(5)结束时要求读者采取具体行动。
-
第8题:

The author cites Maslow’s theory in order to( )A.show the theory can be applied to the energy issue.
B.prove the theory is reasonable.
C.prove that India Gandhi was right with her idea.
D.explain the reason for the comeback of those controversial energy sources.答案:D解析:例证题。作者引用马斯洛理论是为了说明那些有争议的能源被再次利用的原因。 -
第9题:
A client has a need to look at and add many image files but has no need to change them. Which of the following media types would BEST meet the client’s needs?()
- A、CD-RW
- B、Disk
- C、Flash
- D、WORM
正确答案:D -
第10题:
问答题Practice 6 ● Your department needs to employ some temporary staff. ● Write an email to the Human Resources Manager: ● saying how many staff you need and giving the date you want them to start ● explaining why you need them ● stating what skills they should have ● Write 40—50 words.正确答案: 【参考范文】
To: Human resource manager
From: J. Darcy
Subject: Temporary staff needed
Dear Sir,
As you know, the number of orders will increase a great deal as it always does before the Spring Festival and we are short of hands for packaging. Seven people are needed before the end of this weekend there will be no special requirements for skills.
Thanks.
Best regards解析: 暂无解析 -
第11题:
单选题It is necessary to find an engineer ______ has skills that meet your needs.Awhom
Bwhich
Cwhose
Dwho
正确答案: B解析:
句意:找一个具备你所需技能的工程师很有必要。本题考查定语从句。句子中的先行词是engineer,其定语从句has skills that meet your needs中缺少主语。只能是who。whom在句子中引导宾语。根据句意,正确的答案为D。 -
第12题:
单选题Maslow argues that people’s needs _____.Aare largely intangible
Bare fundamental ones
Ccover a wide range
Dvary amongst individuals
正确答案: C解析:
在第二段中,Maslow提出,人的需要是多种多样的,既有心理的需要又有更为抽象的愿望(自我实现)的需要,而且需要是按等级来排列的。因此,C应是正确答案。 -
第13题:
(b) Explain why Oliver might legitimately feel he has a grievance against his manager and identify which aspects
of the formal disciplinary procedure David Morgan did not follow or allow in this case. (9 marks)
正确答案:
Part (b):
Oliver may feel he has a grievance as a consequence of treatment which he perceives as unfair. Proper disciplinary procedures are
essential for harmonious relationships between management and all staff. Oliver may feel that he has been singled out and that
David Morgan does not understand the need for equity in invoking disciplinary procedures.
David Morgan did not follow this procedure. No informal talk took place which might have resolved the problem, preferring to
deliver an oral warning, then moving to a written warning and dismissal. Oliver was not represented and his dismissal is likely to
lead to dissatisfaction with Oliver’s peers.
Oliver must now invoke the correct grievance procedure. -
第14题:
(b) Explain Mintzberg’s five organisational components. (10 marks)
正确答案:
(b) The strategic apex is the highest level of the organisation and is therefore the highest level of management. This part ensures that the organisation’s mission is followed and manages the relationship with the environment.
The operating core is the part that represents the productive activity of the organisation, gathering inputs and, through conversion, turns them into outputs.
The middle line represents that part of the organisation where the middle managers operate. The role of this part is to turn the instructions of the strategic apex into activities for the operating core.
The technostructure includes the staff who provide a technical or supportive activity but which are not a part of the core activities. This part of the organisation includes the engineering, accounting and human resource departments.
The support staff carry out the ancillary activities that are neither part of the core nor the technostructure. Support staff have no role in the direct activities of the organisation: these activities include catering and public relations.(Students may draw the appropriate diagram)
-
第15题:
(b) Explain what is meant by McGregor’s
(i) Theory X; (5 marks)
正确答案:
(b) Douglas McGregor has suggested that the managers’ view of the individuals’ attitude to work can be divided into two categories, which he called Theory X and Theory Y. The style. of management adopted will stem from the view taken as to how subordinates behave. However, these two typologies are not distinct; they do in fact represent the two ends of a continuum.
(i) Theory X is based on traditional organisational thinking. It assumes that the average person is basically indolent and has an inherent dislike of work which should be avoided at all costs. The individual lacks ambition, shuns responsibility, has no ambition and is resistant to change. This theory holds that the individual seeks only security and is driven solely by self-interest. It follows that because of this dislike of work, most have to be directed, controlled, organised or coerced. Management is based on fear and punishment and will have an exploitative or authoritarian style. This reflects the thinking of the classical school of management, based on a scientific approach, specialisation, standardisation and obedience to superiors.
-
第16题:
(c) Explain how absolutist (dogmatic) and relativist (pragmatic) ethical assumptions would affect the outcome
of Anne’s decision. (6 marks)
正确答案:
(c) Absolutism and relativism
Absolutism and relativism represent two extreme positions of ethical assumptions.
Definitions
An absolutist assumption is one that believes that there are ‘eternal’ rules that should guide all ethical and moral decision
making in all situations. Accordingly, in any given situation, there is likely to be one right course of action regardless of the
outcome. An absolutist believes that this should be chosen regardless of the consequences or the cost. A dogmatic approach
to morality is an example of an absolutist approach to ethics. A dogmatic assumption is one that is accepted without
discussion or debate.
Relativist assumptions are ‘situational’ in nature. Rather than arguing that there is a single right choice, a relativist will tend
to adopt a pragmatic approach and decide, in the light of the situation being considered, which is the best outcome. This will
involve a decision on what outcome is the most favourable and that is a matter of personal judgment.
Outcomes
If Anne were to adopt absolutist/dogmatic assumptions, she would be likely to decide that she would need to pursue what
she perceives is the right course of action regardless of cost to herself or the relationship with the client or her manager. Given
that she unearthed a suspect and unaccounted-for payment, and that she received an inadequate explanation from the client,
she would probably recommend extension to the audit beyond the weekend.
If Ann were to adopt relativist or pragmatic assumptions, she would have a potentially much more complicated decision to
make. She would have to decide whether it was more important, ethically, to yield to the pressure from Zachary in the
interests of her short-term career interests or ‘hold out’ to protect the interests of the shareholders. Anne could recommend
sign off and trust the FD’s explanation but she is more likely to seek further evidence or assurance from the company before
she does so. -
第17题:
A new internal auditor, Daisy Rosepetal, has recently joined Bluebell Co. She has been asked by management to
establish and to monitor a variety of social and environmental Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Daisy has no
experience in this area, and has asked you for some advice. It has been agreed with Bluebell Co’s audit committee
that you are to provide guidance to Daisy to help her in this part of her role, and that this does not impair the
objectivity of the audit.
(c) Recommend EIGHT KPIs which could be used to monitor Bluebell Co’s social and environmental
performance, and outline the nature of evidence that should be available to provide assurance on the
accuracy of the KPIs recommended. Your answer should be in the form. of briefing notes to be used at a
meeting with Daisy Rosepetal. (10 marks)
Note: requirement (c) includes 2 professional marks.
正确答案:

-
第18题:
Go to your uncle’s home and see if he needs your help. (英译汉)
参考答案:到你叔叔家去一趟,看看他是否需要你帮忙。
-
第19题:
Swim Co offers training courses to athletes and has prepared the following breakeven chart:
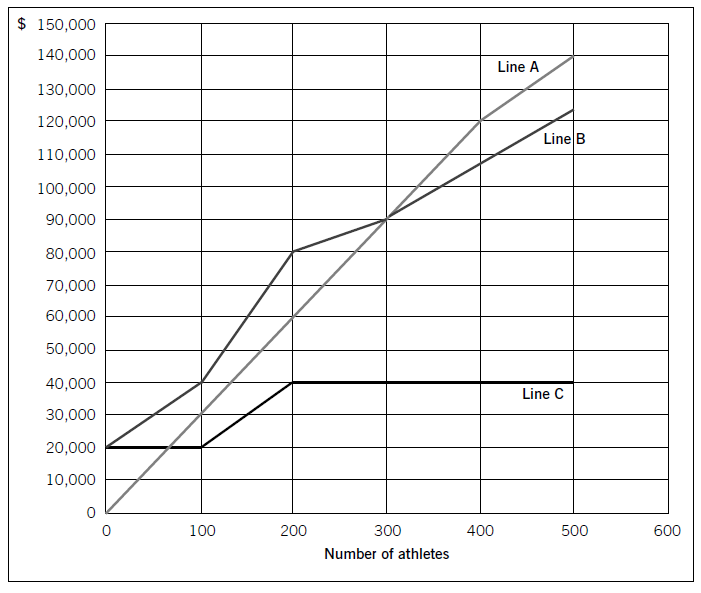
Required:
(a) State the breakeven sales revenue for Swim Co and estimate, to the nearest $10,000, the company’s profit if 500 athletes attend a training course. (2 marks)
(b) Using the chart above, explain the cost and revenue structure of the company. (8 marks)
正确答案:
(a)ThebreakevensalesrevenueforSwimCois$90,000.Thecompany’sprofit,tothenearest$10,000,if500athletesattendthecourseis$20,000($140,000–$120,000).(Fromthegraph,itisclearthatthepreciseamountwillbenearer$17,000,i.e.$140,000–approximately$123,000.)(b)CoststructureFromthechart,itisclearthatLineCrepresentsfixedcosts,LineBrepresentstotalcostsandLineArepresentstotalrevenue.LineCshowsthatinitially,fixedcostsare$20,000evenifnoathletesattendthecourse.Thisleveloffixedcostsremainsthesameif100athletesattendbutoncethenumberofattendeesincreasesabovethislevel,fixedcostsincreaseto$40,000.LineBrepresentstotalcosts.If100athletesattend,totalcostsare$40,000($400perathlete).Since$20,000ofthisrelatestofixedcosts,thevariablecostperathletemustbe$200.Whenfixedcostsstepupbeyondthispointatthelevelof200athletes,totalcostsobviouslyincreaseaswellandLineBconsequentlygetsmuchsteeper.However,sincetherearenow200athletestoabsorbthefixedcosts,thecostperathleteremainsthesameat$400perathlete($80,000/200),eventhoughfixedcostshavedoubled.If300athletesattendthecourse,totalcostperathletebecomes$300each($90,000/300).Sincefixedcostsaccountfor$40,000ofthistotalcost,variablecoststotal$50,000,i.e.$166·67perathlete.So,economiesofscaleariseatthislevel,asdemonstratedbythefactthatLineBbecomesflatter.At400athletes,thegradientofthetotalcostslineisunchangedfrom300athleteswhichindicatesthatthevariablecostshaveremainedthesame.Thereisnofurtherchangeat500athletes;fixedandvariablecostsremainsteady.RevenuestructureAsregardstherevenuestructure,itcanbeseenfromLineAthatfor100–400athletesthepriceremainsthesameat$300perathlete.However,if500athletesattend,thepricehasbeenreducedasthetotalrevenuelinebecomesflatter.$140,000/500meansthatthepricehasgonedownto$280perathlete.Thiswasobviouslynecessarytoincreasethenumberofattendeesandatthispoint,profitismaximised.1 -
第20题:
A user is attempting to connect to the network remotely using a laptop and dial-up. The user plugsthe cable into the only available laptop connection, but the connector is loose inside the port. TheMOST likely reason the connector is loose is the:()
- A、RJ-11 connector needs to be re-crimped
- B、User has plugged into the laptop's NIC port
- C、User has plugged the wrong end of the cable into the port
- D、RJ-11 connector needs to be replaced with an RJ-45 connector
正确答案:B -
第21题:
单选题According to Maslow, what are “arranged in a hierarchy”?APhysiological drives.
BAn individual’s motives.
CAn individual’s needs.
DAbstract desires.
正确答案: B解析:
本题线索在第二段第二句“but also that they are arranged in a hierarchy whereby the lower order needs must ... play.”,句中“whereby”一词的意思是“凭借该等级”,故“按等级排列的”不应是需要,而应是动机。 -
第22题:
单选题1It is necessary to find an engineer ______ has skills that meet your needs.Awhom
Bwhich
Cwhose
Dwho
正确答案: C解析:
本题考查定语从句。句子中的先行词是engineer,其定语从句has skills that meet your needs中缺少主语。只能是who。whom在句子中引导宾语。根据句意,正确的答案为D。句意:找一个具备你所需技能的工程师很有必要。 -
第23题:
问答题1) The hierarchy of needs is an idea associated with one man, Abraham Maslow, the most influential humanist ever to have worked in industry.It is a theory about the way in which people are motivated. 2) The theory arose out of a sense that classic economics was not giving managers much help because it failed to take into account the complexity of human motivation. Maslow divided needs into five: · Physiological needs: hunger, thirst, sex and sleep. Food and drinks manufacturers operate to satisfy needs in this area, as do prostitutes and tobacco growers. · Safety needs: job security, protection from harm and the avoidance of risk. At this level an individual’s thoughts turn to insurance, burglar alarms and savings deposits. · Social needs: the affection of family and friendship. These are satisfied by such things as weddings, sophisticated restaurants and telecommunications. · Esteem needs (also called ego needs), divided into internal needs, such as self-respect and sense of achievement, and external needs, such as status and recognition. Industries focused on this level include the sports industry and activity holidays. · Self-actualization, famously described by Maslow: “A musician must make music, an artist must paint, a poet must write, if he is to be ultimately happy. What a man can be, he must be. This need we may call self-actualization.” Self-actualization is different from the other levels of need in at least one important respect: it is never finished, never fully satisfied. 3)It is, as Shakespeare put it, “as if increase of appetite grows by what it feeds on”. An individual’s position in the hierarchy is constantly shifting and any single act may satisfy needs at different levels. Thus having a drink at a bar with a friend may be satisfying both a thirst and a need for friendship (levels one and three). Single industries can be aimed at satisfying needs at different levels. For example, a hotel may provide food to satisfy level one, a nearby restaurant to satisfy level three, and special weekend tours of interesting sites to satisfy level five. The hierarchy is not absolute. It is affected by the general environment in which the individual lives. The extent to which social needs are met in the workplace, for instance, varies according to culture. 4) In Japan the corporate organization is an important source of a man’s sense of belonging (although not of a woman’s); in the West it is much less so.One of Maslow’s early disciples was a Californian company called NLS (Non-Linear Systems). In the early 1960s it dismantled its assembly line and replaced it with production teams of six or seven workers in order to increase their motivation. 5) Each team was responsible for the entire production process, and they worked in areas that they decorated according to their own taste. A host of other innovations (such as dispensing with time cards) revolutionized the company. Profits and productivity soared, but Maslow remained skeptical. He worried that his ideas were being too easily “taken as gospel truth, without any real examination of their reliability”.(此文选自The Economist 2008年刊)正确答案:
(1)【答案】提到需求层次理论,我们便会想到迄今为止在人类学研究领域最富影响力的一个人——亚伯拉罕·马斯洛。
【解析】本句是一个单句:The hierarchy of needs is an idea associated with one man,句中one man有两个同位语,因此重点在确定句子的顺序。首先,根据中英文行文差异:英文先出最重要信息,然后才是次要信息,最后是补充信息,中文正好与之相反可知,本句主语之后首先出现的应该是man的第二个同位语,然后是第一个同位语;其次,注意industry此处不是表示“工业”,而是指“某研究领域”。
(2)【答案】古典经济学因为没能考虑到人类复杂的动机和需求,所以不能给管理者提供多少帮助,需求理论便应运而生。
【解析】本句由主句+定语从句构成,其中定语从句有状语从句,需理清句子顺序。首先,和上题一样的方法确定译句的顺序,because从句最先译出,然后是定语从句中的主句,最后是主句;其次,音译汉时,记住一定先出主语,故classic economics最先译;最后,本句the complexity of human motivation中,将抽象名词complexity根据其形容词词根译为“复杂的”,此处涉及到英译汉“偏正互换”的技巧,原文用human motivation修饰complexity,本该是“人类动机的复杂性”,但根据中文特点,则译为“复杂的人类动机”,即改变两者地位,使译文更加地道。
(3)【答案】如莎士比亚所说,在这个方面,“吃得越好,胃口也就越好”。
【解析】本句由单句+方式状语从句构成,只是状语插入到主句当中了,因此,应先确定句子顺序,重点是主句后半句的翻译。首先,次要信息as放句首,接着出主句;其次,主句中it可以用代词“不抽象不具体”的译法,即不抽象译为“它”,也不具体译为“自我实现”使译文累赘,可译为不抽象不具体的“这方面”;最后,引言中按照动作发生的先后顺序进行翻译。
(4)【答案】在日本,对于一个男人,公司是归属感的一个重要来源(虽然对于女人不是这样);而在西方,这种情况则远非如此。
【解析】本句由两个并列单句组成,翻译时注意单句之间的衔接。首先,句中的man应该用本义“男性”,这样与woman相对应;其次,第二句中it代指上一句所提到的现象,故不抽象不具体地译为“这种情况”,so 也是上句提到的情况,译成“如此”,避免重复;最后,两句之间根据内容可以判断是对比关系,用转折连词“而,但是”是文意更加流畅。
(5)【答案】每个小组都对整个生产过程负责,并且他们工作的地方是按照他们自己喜欢的风格装修的。
【解析】本句由and连接两句子构成,是并列关系,故可按原文顺序直接译,注意第二句中定语从句的翻译。解析: 暂无解析
